According to Stratview Research, the 3D Printing Construction Market is segmented by Construction Method Type (Extrusion, Powder Bonding), by Material Type (Concrete, Metal, Composite, and Others), by End-Use Sector Type (Building, Infrastructure), and by Region (North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and Rest of the World).
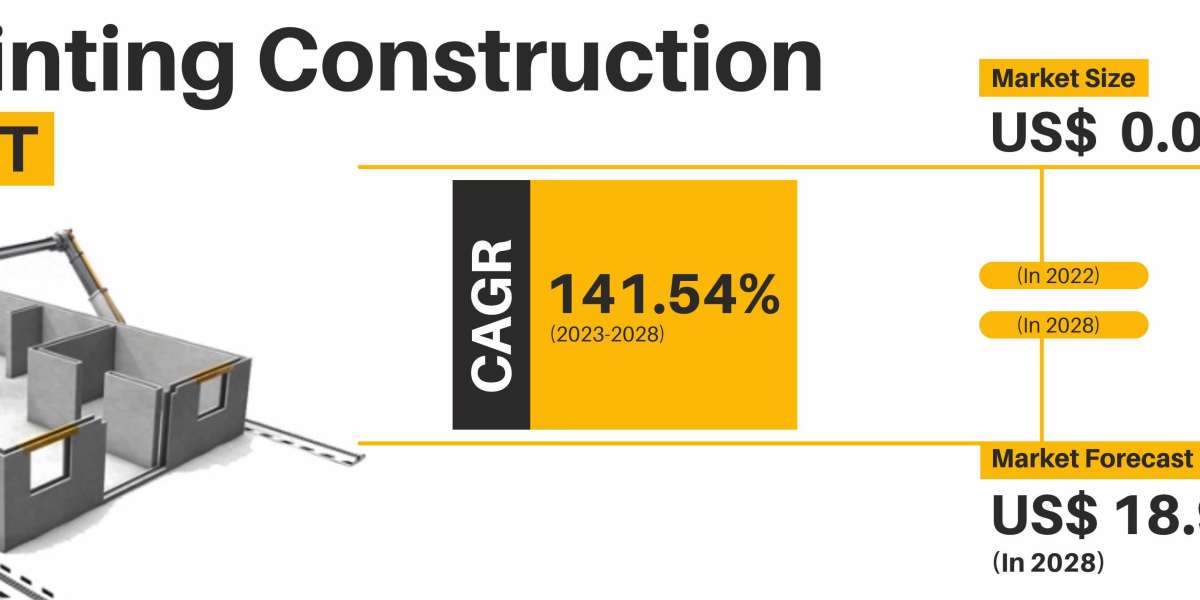
The 3D printing construction market was estimated at USD 0.08 billion in 2022 and is likely to grow at a CAGR of 141.54% during 2023-2028 to reach USD 18.91 billion in 2028.
Innovation is the driving force behind progress, and the construction industry is no exception. As technology continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, new and innovative construction techniques are emerging, revolutionizing the way we build. One such technique that is gaining significant traction is 3D printing. In this article, we will take a closer look at the growing role of 3D printing in construction and explore how this groundbreaking technology is reshaping the industry.
Additive Manufacturing in Construction:
At its core, 3D printing in construction relies on additive manufacturing, a process that involves building structures layer by layer using specialized printers. This technique offers numerous advantages over traditional construction methods. By eliminating the need for formwork and enabling the direct translation of digital designs into physical structures, 3D printing reduces construction time, minimizes material waste, and enhances precision. Additive manufacturing allows for greater flexibility and efficiency in construction, leading to cost savings and improved project outcomes.
Prefabrication and On-Site Printing:
3D printing in construction encompasses two primary approaches: prefabrication and on-site printing. Prefabrication involves printing building components, such as walls, floors, or facades, in an off-site factory before transporting and assembling them at the construction site. This method offers the benefits of controlled manufacturing conditions, increased production speed, and improved quality control. On the other hand, on-site printing involves directly printing the structure at the construction site itself. This approach provides greater flexibility, adaptability, and the ability to construct large-scale buildings that would be challenging to transport. Both methods have their advantages, and their applications depend on project requirements and logistical considerations.
Bridging Design and Construction:
3D printing in construction has the unique ability to bridge the gap between design and construction processes. Through the use of Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, architects and engineers can create intricate and complex designs that can be directly translated into 3D printable files. This seamless integration enables more efficient collaboration between designers and builders, reducing errors, and streamlining the construction workflow. The direct link between design and construction facilitates enhanced communication, accurate cost estimation, and better project planning, resulting in smoother project execution and improved outcomes.
Materials and Structural Innovations:
One of the key challenges in 3D printing for construction has been the development of suitable materials that can withstand structural requirements while maintaining printability. However, significant progress has been made in this area. Researchers and industry professionals are experimenting with a wide range of materials, including concrete mixes, polymers, and composites, to create durable, lightweight, and environmentally friendly building components. Additionally, 3D printing enables the incorporation of complex geometries and internal structural features, such as voids and reinforcement patterns, which can enhance the overall strength and performance of the printed structures. These material and structural innovations pave the way for a new era of architectural design and construction possibilities.
The Future of Construction:
As 3D printing continues to advance, its role in the construction industry is set to expand even further. We can envision a future where entire neighborhoods are printed on-demand, customized structures cater to individual needs, and sustainable materials are widely adopted. The potential for increased affordability, reduced construction timelines, and enhanced design freedom is immense. However, challenges remain, such as scaling up the technology, ensuring regulatory compliance, and addressing workforce skills. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial in realizing the full potential of 3D printing and transforming the construction industry.