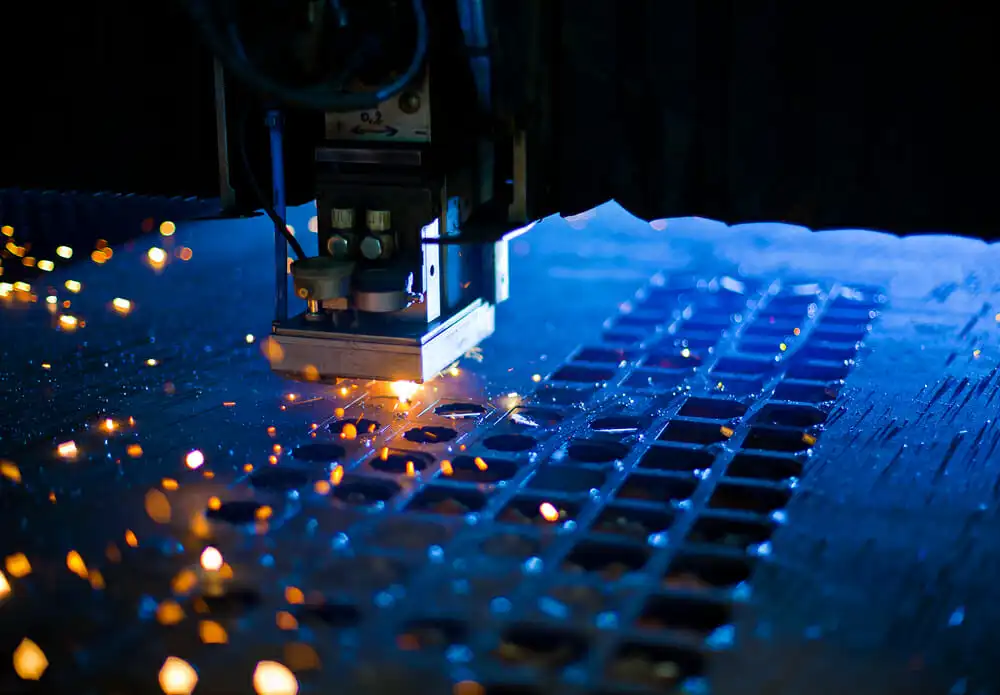
What do you think of when you hear the word "laser"? For many people, lasers conjure images of Star Wars lightsabers and sci-fi movies. But many industries use laser technology as a tool in their manufacturing processes. In fact, you've almost certainly come across products made with a laser cutter. For example many people use the Ortur Laser Master 3 for their laser engraving business.
Although laser cutting may seem like a modern technology, the history of laser cutting may surprise you. The first lasers originated from Einstein's theoretical work and followed a fascinating path before becoming the higher power lasers used in many industries today. Let's trace the history of laser cutting, from Einstein to the first working laser, to the modern day.
What is Laser Cutting?
Laser cutting is a technique for cutting or engraving hard materials by burning, melting or vaporizing. The process has a variety of industrial applications in various industries and can be used to drill holes or cut shapes in metal and other materials on the production line. Laser cutting is also used as an artistic technique for engraving decorative patterns on surfaces. Using various types and functions of laser engraver to achieve personalized customization, Ortur has grown slowly from a small company with a few people to the current leader in the laser engraving machine industry. Ortur Laser Master 3 has become the most popular laser engraving machine One of the engraving and cutting machines.
The main advantage of laser cutting technology is its accuracy, a high power beam is focused through a laser cutting nozzle for precise positioning. Modern laser cutting often uses CAD technology, allowing artists and engineers to create complex designs using industrial lasers. Then transfer it into Ortur Laser Master 3 and wait for the completion of printing. You can also operate the printing process of Ortur Laser Master 3 through the touch screen.
How Does Laser Cutting Work?
Close-up view of a laser cut paper pattern - History of Laser Cutting Lasers work by exciting atoms in a solid, liquid or gaseous medium. This requires an energy pump, which could be an electric current, or even a second laser. When the atoms in the medium absorb energy, they begin to glow. The light is concentrated by placing a mirror at each end of the medium, forming an optical cavity.
Laser cutting works by focusing a laser beam onto a sheet metal or other hard material. Mirrors, lenses and compressed gas such as carbon dioxide allow technicians to adjust the focus of the laser beam through the laser cutting nozzle.
The narrow beam then melts or burns away the material, and the technician can then move on to the next area by moving the cut material or the laser head. CAD technology allows the automatic movement of the laser head through cutting sheet metal or other materials.
What types of laser cutting machines are there?
A laser cutter is defined by its laser medium. Solid-state lasers use materials such as ruby or glass to produce a focused laser beam. Gas laser cutting uses gas (usually CO2), while liquid laser requires a liquid medium. The most common types of laser cutting are:
Gas laser cutting: The gas laser cutting process is often referred to as CO2 laser cutting. A CO2 laser cutter emits a laser beam through a CO2 mixture. This technique is commonly used for cutting non-metallic materials such as wood.
Crystal Laser Cutting: Crystal laser cutting machines can cut and engrave a variety of materials, including metal and non-metal surfaces. However, they are not particularly durable and expensive to build and run.
Fiber laser cutting: Fiber laser cutting machine is a recently invented laser machine. The machines use a medium made of fiber optics and are less expensive to manufacture than gas or crystal laser cutters. Another advantage of fiber lasers is their higher power output. This economical cutting tool is suitable for a variety of metallic and non-metallic materials.
Who Invented Laser Cutting?
The history of laser cutting dates back to 1917, when Albert Einstein proposed the theory of "stimulated emission of radiation," the principle behind modern lasers. His theory is that when electrons absorb enough energy to raise an energy level within an atom, they can emit photons.
In 1959, a scientist named Gordon Gould extended Einstein's theory. He suggested that stimulated emission of radiation could be used to amplify light. His theory was called "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation" - or "LASER" for short.
Jump forward in time to 1960, when Theodore Maiman created the first-ever working laser in his California lab. He used synthetic rubies to produce crimson beams, although many of his contemporaries could not see the use for his ruby lasers. In fact, the technology has been described as a "solution to a problem" and has been questioned and even skeptical by the public. However, many members of the scientific community saw potential in Maiman's invention, including scientists at Bell Laboratories in New Jersey.
It wasn't until 1964 that a scientist at Bell Laboratories finally developed thermal cutting using lasers. Kumar Patel invented a gas laser cutting process using a carbon dioxide mixture and found it to be a faster and more cost-effective improvement on laser cutting rubies. His colleague JE Geusic at Bell Labs invented the crystal laser process later that year. The invention captured the popular imagination and featured in a famous scene in the 1964 film "Goldfinger," in which the titular villain attempts to split James Bond in two with a laser beam.
Who Were the First Groups to Use Laser Cutters?
The first group to use laser cutting was the Western Engineering Research Center in Buffalo, New York in 1965. The group wanted to find a more efficient way to make the wires. Back then, manufacturers used diamond dies to extrude metal wire, and die holes were expensive, difficult and time-consuming to drill.
Western Engineering Research Center pioneered the use of focused laser beam cutting to drill holes faster. This was a pivotal moment in the history of laser cutting, paving the way for other companies to explore the potential uses of laser technology. Much of the group's work has focused on discovering more about the safety of laser beams and their potential impact on human health.
History of Laser Cutting Use
Shortly after Western Engineering Research Center began using laser cutting as a drilling technique, scientists developed gas laser cutting using carbon dioxide. This development makes laser cutting technology more versatile. The development of lasers capable of cutting metals such as mild steel is particularly important for the widespread adoption of the technology.
In 1969, Boeing became the first company to commercialize gas laser cutting. Three of its employees co-authored a paper exploring the concept of using CO2 lasers to cut titanium, Hastelloy and ceramics. This paper led to the development of multi-beam laser cutting, and Boeing began using laser beams on its production line as an efficient cutting process. Western Electric began mass producing cutting machines widely used in the aerospace industry in the 1970's.
The use of gas laser cutting became common in the 1980s. It is thought that around 20,000 industrial laser cutting machines were in use during this period, with a total value of around $7.5 billion. In fact, laser cutting technology has revolutionized the production industry to such an extent that Professor Bill Steen says their invention marks the beginning of a new industrial revolution.
In 1979, we ushered in another pivotal moment in the history of laser cutting. Before this, laser cutting was two-dimensional. Prima Industrie of Collegno, Italy has invented a 3D laser cutting technology that significantly expands the potential applications of laser cutting technology.
Laser Technology Today
Laser cutting has come a long way since Boeing produced laser-drilled dies in the late 60s. Today, laser power supplies are widely used in various industries, especially automobile manufacturing. Advances in laser cutting technology mean the technique can be used on thicker and more varied materials, from metals to ceramics and even paper. Fiber optic and CO2 laser cutting methods allow manufacturers to cut materials faster than previous technologies, allowing them to scale up production while reducing man hours.
Just look around your home and you will almost certainly find products that have been cut or engraved using a laser. Many industries use lasers to engrave logos or text on products, such as the letters on a computer keyboard.
What's Next?
Laser Cutting Acrylic Machine Close Process This is not the end of the development of laser cutting technology. Engineers and scientists are constantly innovating, which may lead to the development of more powerful laser cutting machines with increased thickness capabilities, cutting speed and precision. Advances in automation will allow production lines to run unattended 24 hours a day and provide a safer working environment for technicians using laser cutters.
Talk to a Laser Cutter Expert
Laser cutting is a fascinating technology with an interesting and often surprising history. To take full advantage of this precise and efficient technology, you need the right equipment.
HTPOW is the first-class distributor of high-performance fiber laser cutting machines in the United States. Whether you need a machine for etching, engraving or cutting, HTPOW can help you find the right product for your unique requirements. Get in touch with the professional customer service team to discuss your needs and discover how the right laser cutting machine can benefit your business.