Introduction:
Disease outbreaks in animals can have severe consequences, not only for animal health but also for human health, food security, and the economy. Veterinary vaccines play a crucial role in preventing and controlling disease outbreaks, protecting both animal populations and public health. This article explores the significance of veterinary vaccines in preventing disease outbreaks and highlights their impact on animal welfare and public safety.
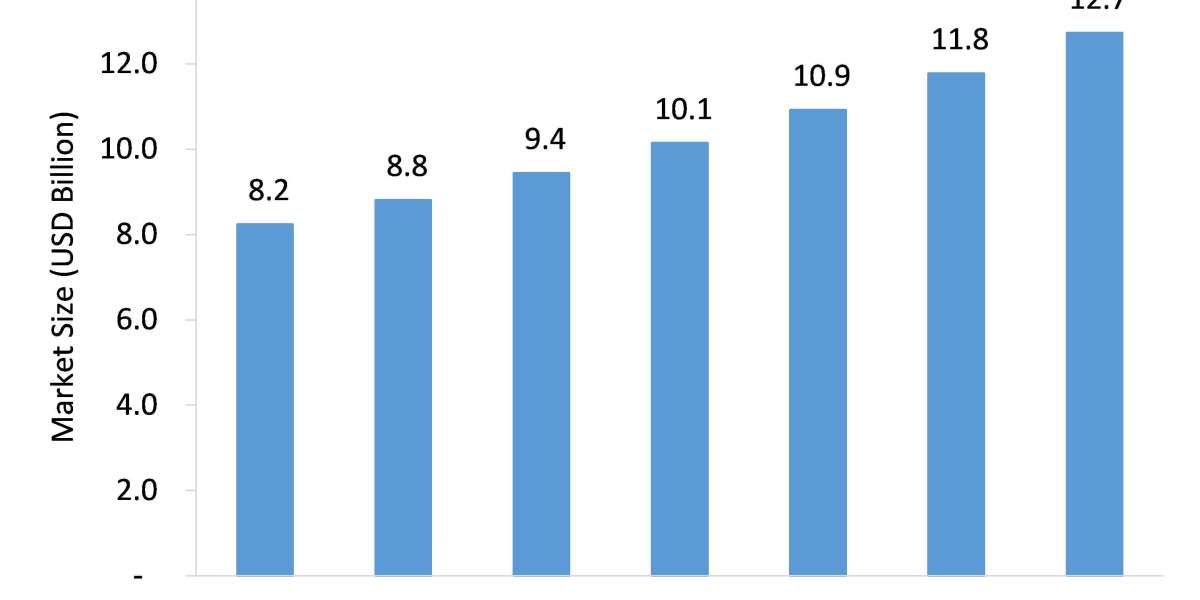
The Global Veterinary Vaccines Market is projected to grow from USD 8.24 billion in 2020 to USD 12.81 billion by 2026 at a CAGR of over 7.6% during the forecast period.
Read more: https://www.stratviewresearch.com/1702/veterinary-vaccines-market.html
Disease Prevention and Control:
Veterinary vaccines are a powerful tool in preventing and controlling infectious diseases in animals. Vaccination stimulates the immune system, enabling animals to develop immunity against specific pathogens. By vaccinating animals, disease agents can be effectively targeted, reducing the risk of disease transmission and outbreaks.
Herd Immunity and Disease Spread:
The concept of herd immunity is vital in disease prevention. When a significant proportion of a population is vaccinated, the transmission of infectious agents is hindered, protecting susceptible individuals and reducing the overall disease burden. Veterinary vaccines contribute to the establishment of herd immunity, preventing the rapid spread of diseases within animal populations.
Zoonotic Disease Prevention:
Zoonotic diseases are those that can be transmitted from animals to humans. Veterinary vaccines play a critical role in preventing zoonotic diseases by controlling the disease in animal reservoirs. Vaccinating animals reduces the risk of transmission to humans, protecting public health and preventing potential pandemics.
Protection of Animal Welfare:
Disease outbreaks can have devastating effects on animal welfare. Vaccinating animals helps to prevent suffering and reduce mortality rates associated with infectious diseases. By providing immunity against common pathogens, veterinary vaccines contribute to maintaining the health and well-being of animals, ensuring their quality of life.
Safeguarding Food Safety:
Disease outbreaks in livestock can have significant implications for food safety and security. Vaccination programs targeting livestock ensure the production of safe and healthy food products. By preventing diseases such as avian influenza, foot-and-mouth disease, or bovine tuberculosis, veterinary vaccines contribute to maintaining the integrity of the food supply chain.
Economic Implications:
Disease outbreaks in animals can result in substantial economic losses, affecting both individual farmers and entire industries. Veterinary vaccines offer a cost-effective approach to disease prevention, reducing treatment expenses, production losses, and trade restrictions. By minimizing the occurrence and impact of disease outbreaks, vaccines support the economic sustainability of the livestock and agricultural sectors.
Conclusion:
Veterinary vaccines are indispensable in preventing and controlling disease outbreaks in animals. Their role extends beyond animal health, encompassing public health, food safety, and economic stability. By providing immunity, reducing disease transmission, and safeguarding animal welfare, veterinary vaccines contribute to a safer and healthier environment for both animals and humans. Continued research, education, and vaccination programs are vital in combating emerging and existing infectious diseases, mitigating the risks of disease outbreaks, and ensuring a sustainable future for animal and human populations.