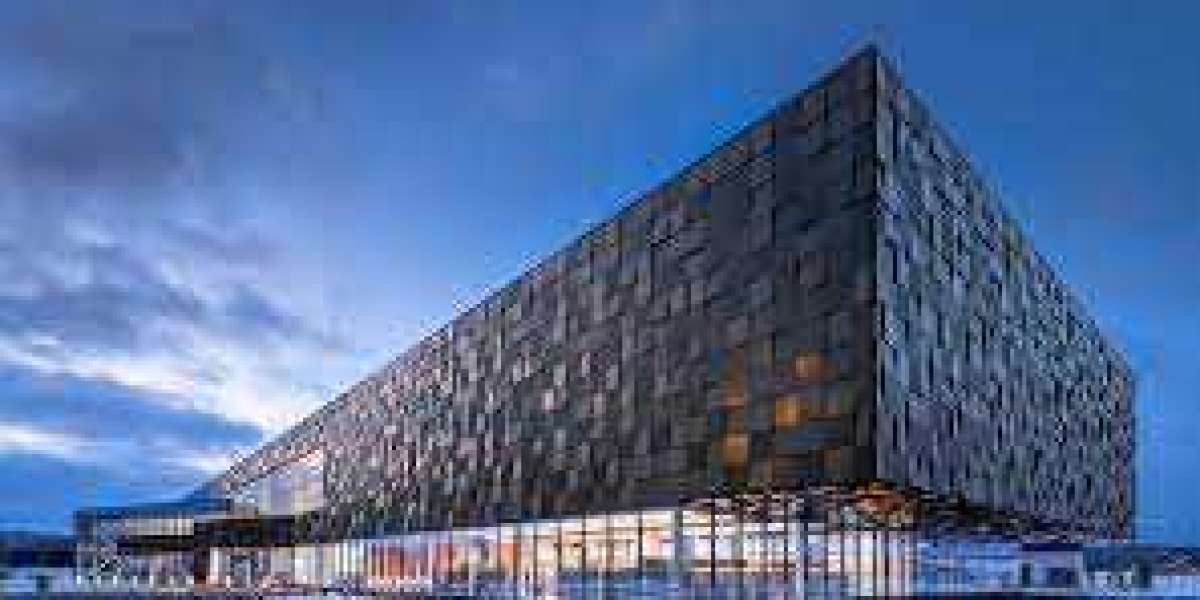
Architectural design has evolved over the years, incorporating new materials and technologies to create structures that not only serve functional purposes but also captivate with their aesthetic appeal. One such innovation that has transformed the landscape of modern architecture is the use of transparent facades, predominantly made of glass. These glass wonders not only redefine the relationship between indoor and outdoor spaces but also contribute to sustainable design and energy efficiency.
The Rise of Transparent Facades
Transparent Architectural Facades have gained immense popularity in recent decades, marking a departure from the conventional use of opaque materials. This shift is driven by a desire to create open, light-filled spaces that foster a connection with the environment. The advent of advanced glass technologies and engineering techniques has made it possible to design structures with expansive glass facades, allowing natural light to flood interiors and offering panoramic views.
Technological Advancements in Glass
The success of transparent facades hinges on the technological advancements in glass manufacturing. Traditional glass has been replaced by high-performance materials such as Low-E (Low Emissivity) glass, which minimizes heat transfer while allowing visible light to pass through. Additionally, smart glass technologies enable dynamic control over transparency, allowing occupants to adjust the tint of the glass based on the external conditions.
Sustainable Design and Energy Efficiency
Transparent facades contribute to sustainable architecture by harnessing natural light, reducing the reliance on artificial lighting during the day. This not only minimizes energy consumption but also creates a healthier indoor environment. Furthermore, the use of energy-efficient glass coatings helps in temperature regulation, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. The integration of photovoltaic glass also allows buildings to generate solar power, promoting sustainability.
Challenges and Solutions
While transparent facades offer numerous benefits, they also present challenges such as heat gain, glare, and privacy concerns. Architects and engineers have responded to these challenges with innovative solutions. Double-skin facades, for instance, create a buffer zone between the interior and exterior glass layers, mitigating heat gain. Smart glass technologies with adjustable transparency address privacy concerns by allowing occupants to control the level of visibility.
Iconic Examples of Transparent Facades
Several iconic structures around the world showcase the transformative power of transparent facades. The Apple Park Headquarters in Cupertino, California, designed by Foster + Partners, features a massive curved glass facade, blurring the boundaries between the workspace and the surrounding natural landscape. The Louvre Abu Dhabi, designed by Jean Nouvel, boasts a stunning latticed dome with a double-layered stainless steel and aluminum roof, allowing diffused natural light to filter through.
Integration with Biophilic Design
Transparent facades align seamlessly with the principles of biophilic design, which seeks to incorporate elements of nature into the built environment. By allowing unobstructed views of the outdoors, these facades create a sense of connection with nature. The use of natural materials in conjunction with glass further enhances the biophilic experience, fostering well-being and productivity among building occupants.
Cultural and Social Implications
The use of transparent facades goes beyond aesthetics and functionality; it has cultural and social implications. Transparent structures often symbolize transparency in governance and corporate practices. Moreover, they invite the surrounding community to engage with the building, breaking down barriers between the public and private realms. The Shard in London, designed by Renzo Piano, exemplifies this idea, as its transparent glass facade reflects the dynamism and openness of the city.
Future Trends and Innovations
As technology continues to advance, the future of transparent architectural facades holds exciting possibilities. Nanotechnology may be employed to create self-cleaning glass surfaces, reducing maintenance costs and ensuring the longevity of these structures. The integration of augmented reality and interactive displays within glass facades could redefine the way we interact with buildings, turning them into dynamic canvases for information and art.
Conclusion:
Transparent architectural facades represent a profound shift in the way we perceive and design buildings. From their humble beginnings to becoming iconic symbols of modern architecture, these glass wonders have not only transformed skylines but also enriched the human experience within built environments. As we continue to push the boundaries of technology and design, the future promises even more breathtaking innovations in the realm of transparent facades, shaping the cities of tomorrow. Whether for sustainability, aesthetics, or cultural significance, the allure of glass in architecture continues to captivate, making these structures true wonders in the world of design.